Xi’an, China – A striking discovery has emerged from the tomb of Emperor Qin Shi Huang, the first Emperor of China, dating back to 210 BCE. Among the extensive collection of terracotta warriors unearthed, a particularly well-preserved figure has been recently found, shedding new light on the remarkable artistry and military legacy of the Qin Dynasty.
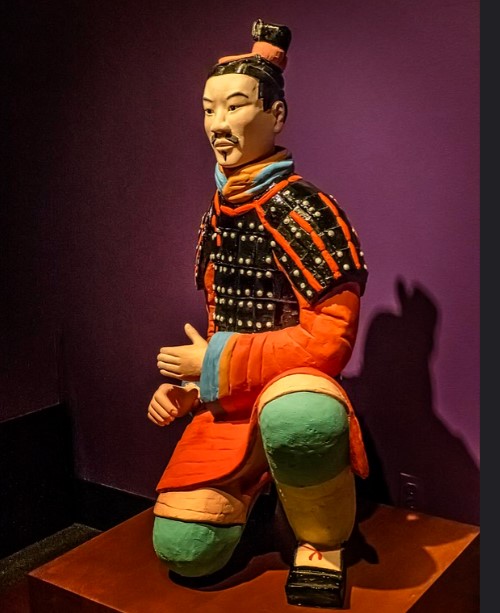

The Discovery
The terracotta warrior was found in the vast necropolis of Emperor Qin Shi Huang, located near the modern city of Xi’an. This archaeological site, known for its army of life-sized terracotta soldiers, is one of the most significant and celebrated discoveries in Chinese history.
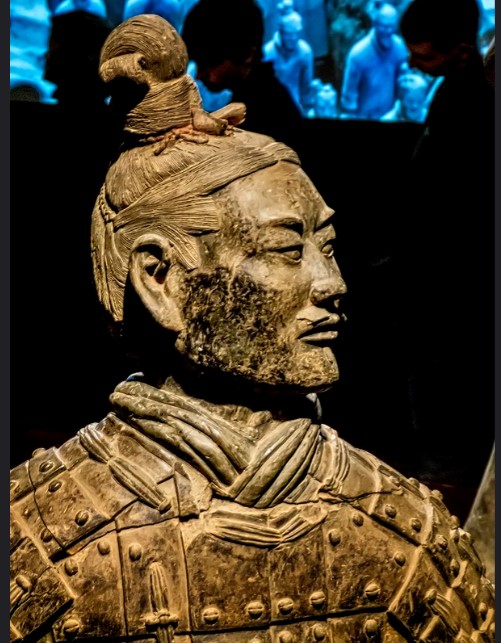

- Excavation Site: The tomb complex of Qin Shi Huang spans approximately 56 square kilometers and contains thousands of terracotta figures, including soldiers, horses, chariots, and weapons. The newly discovered warrior was unearthed during recent excavations aimed at further exploring the tomb’s depths.
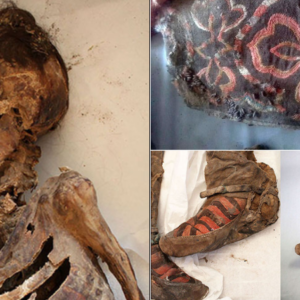
- Condition of the Warrior: This warrior is remarkably well-preserved, with detailed features and remnants of original paint still visible, offering a rare and vivid glimpse into the past.

Description of the Terracotta Warrior
The terracotta warrior exemplifies the extraordinary craftsmanship and meticulous detail characteristic of these ancient sculptures.
- Design and Features: The warrior stands approximately 6 feet tall and is depicted in a dynamic pose, ready for battle. The figure’s facial features are finely carved, each unique and thought to represent real soldiers of the time. The warrior is dressed in detailed armor, indicative of the military attire worn by Qin soldiers.

- Materials and Craftsmanship: Made from terracotta clay, the warrior was created using a combination of mᴀss-production techniques and individual hand-finishing. This method allowed for both uniformity and personalized detail. Traces of pigments on the warrior suggest that it was originally painted in vibrant colors, adding to its lifelike appearance.