The 2,500-year-old mummy of a Scythian princess, discovered in Siberian permafrost 21 years ago, is to be returned to its original resting place amid local criticism over natural disasters. The decision comes after decades of scientific study and heated debates over the animal’s cultural and spiritual significance.

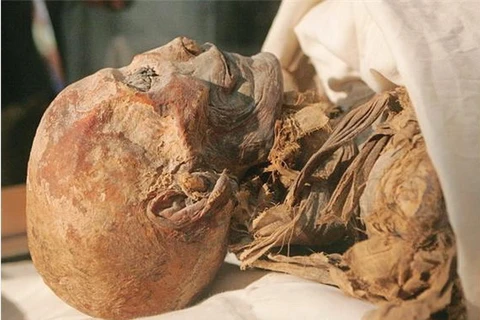
Discovered in 1993, the princess’s remarkably well-preserved body was found in a burial mound on the Ukok plateau. Her ornate tattoos, luxurious clothing and accompanying artefacts provided valuable imagery to Scythian culture. However, the decision to remove her from her resting place has sparked controversy among local Protestant groups who believe her spirit has been affected by the disturbance.
According to local legends, the princess was buried in the permafrost to prevent evil spirits from invading the world of the living. Some believe that recent natural disasters in the region are a result of disturbing her eternal slumber. To appease the spirits and prevent further calamities, local elders have called for the princess’s return.
The scientists have agreed to repatriate the mummy and build a new burial site that respects traditional Scythian burial customs. The new tomb will be located on the Ukok plateau, at an alтιтude of 2,500 meters, and will be accessible to researchers for future studies.
The decision to return the treasure to its homeland marks a significant shift in the approach to archaeological discoveries. It recognises the importance of the cultural heritage and spiritual beliefs of indigenous peoples. As scientists seek to learn more about the Scythians and their customs, it is essential to balance the pursuit of knowledge with respect for the past.
The repatriation of the Siberian Ice Maiden serves as a reminder that archaeological discoveries are not simply objects of scientific study, but also have deep cultural and spiritual significance. By honoring the wishes of the local community, scientists are demonstrating a commitment to ethical research and a respect for the diverse cultures of our planet.