Water supply systems have always played a crucial role in human development, and both ancient and modern civilizations have made significant contributions to improving the quality of life through the provision of clean water. One of the most notable engineering feats of ancient Rome was its aqueduct systems, which were instrumental in delivering water to urban areas. In contrast, modern water supply systems rely on electric pumps and advanced materials to transport water more efficiently.
Ancient Water Supply Systems: Relying on Gravity
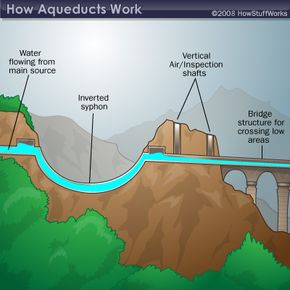
The ancient Romans built impressive aqueducts to transport water from distant sources to cities. One of the remarkable aspects of these aqueducts was that they primarily depended on gravity, meaning that water flowed naturally from higher elevations to lower ones without the need for mechanical pumps.
Roman aqueducts were designed with a very slight downward slope, ensuring that the water would flow continuously over long distances. These aqueducts were carefully constructed to pᴀss over various terrains, from flat plains to hilly landscapes, often using stone bridges to maintain the necessary gradient. The Romans also designed these systems with great attention to detail, ensuring that the water would not leak, and often included maintenance structures along the way.
The water delivered by these aqueducts was used not only for drinking but also for public baths, fountains, and private homes, as well as for sewage systems. This system was central to Roman urban life, contributing to the health and prosperity of their cities.
Modern Water Supply Systems: Powered by Electric Pumps
In contrast to the Roman reliance on gravity, modern water supply systems predominantly use electric pumps to move water from its source to urban areas. This method allows for greater control over the flow and pressure of the water, which is especially important when the terrain is challenging or when water needs to be transported over very long distances or to higher elevations.
Modern pumps can push water up slopes and through miles of pipelines, overcoming the limitations of terrain that would have made Roman aqueducts impractical in certain situations. The use of electric pumps also makes it easier to manage the water distribution more precisely, ensuring that water reaches homes, industries, and agricultural areas effectively.
Moreover, the advancements in materials such as plastic and steel have allowed for more durable and efficient water pipes compared to the stone and lead used in ancient systems. This enables modern water systems to serve large populations with less maintenance and greater reliability.
Comparing Both Systems
Although Roman aqueducts were an extraordinary achievement for their time, modern water supply systems have far surpᴀssed them in terms of efficiency, scale, and flexibility. Electric pumps and modern technologies allow for a more precise and controlled distribution of water, even in areas with complex topography or high demand.
However, this does not diminish the historical significance of Roman aqueducts. They are a testament to the ingenuity and engineering capabilities of the Romans, showcasing their ability to harness natural forces to meet the needs of their cities.
Conclusion
Both ancient and modern water supply systems have been crucial in providing water to humanity, but the differences in their mechanisms are striking. Roman aqueducts were a prime example of using gravity to transport water, while modern systems have embraced technology, specifically electric pumps, to make water delivery faster and more efficient. These advancements in technology have allowed modern water systems to meet the growing demands of a global population, improving living standards around the world.